GENERAL
What’s a Rumble Device Designed to Do for Road Safety
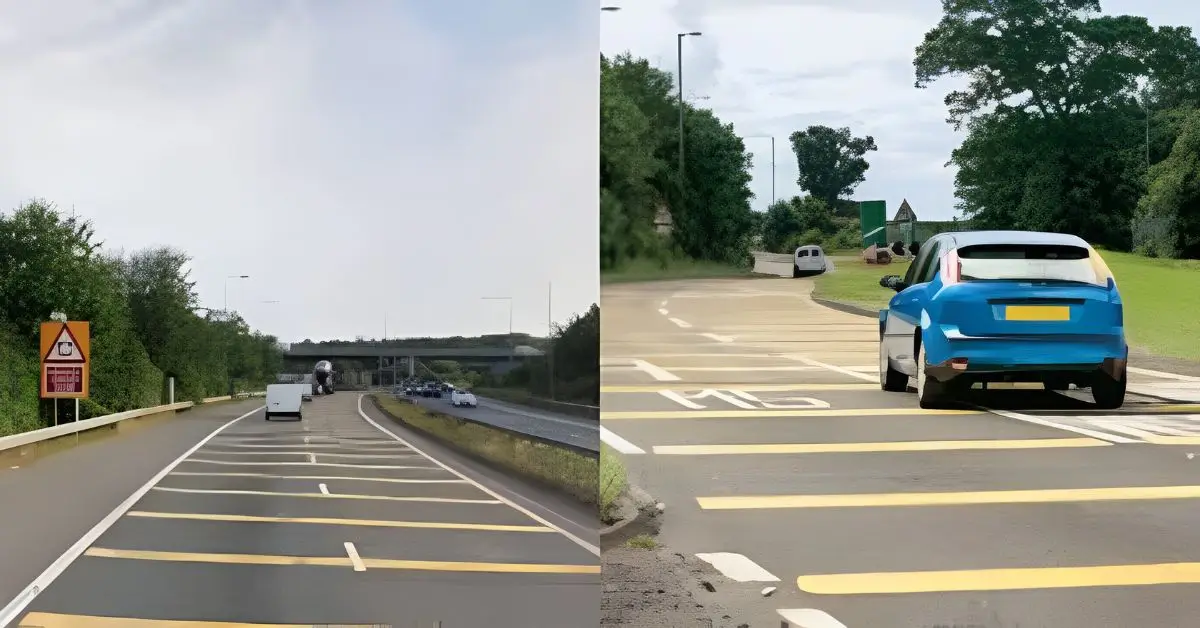

If you’ve ever felt your steering wheel shake and heard a deep growl from beneath your tires, you’ve experienced a rumble device in action. Far from being road damage, these are carefully engineered safety features. For anyone wondering what’s a rumble device designed to do, the answer is simple: it’s built to grab a driver’s attention through three channels at once: touch, hearing, and sight, especially when they drift from a safe path.
According to the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), shoulder rumble strips can cut run-off-road crashes by 20–72%, while centerline versions slash head-on collisions by 44–45%. With benefit cost ratios as high as 54:1, they rank among the most effective and affordable road safety measures in the world.
Quick Answer
A rumble device is designed to warn drivers through vibration, sound, and sometimes visual cues, reducing roadway departure crashes by up to 50%. It’s a low-cost, high-impact safety measure that keeps motorists alert, prevents run-off-road incidents, and saves lives worldwide.
Where and When Was the First Rumble Device Used?
Rumble devices first appeared in 1952 on the Garden State Parkway in New Jersey, aimed at waking up distracted drivers with a vibrating alert under their wheels. These early “singing lanes” scored the pavement’s edge so tires created a whine alerting drivers by sound and feel to drift danger ahead. (Wikipedia)
What’s the Primary Purpose of Rumble Devices on Roads?
For anyone asking what’s a rumble device designed to do, these devices prevent inattentive, drowsy, or distracted driving from turning deadly. They work by creating a sudden, unmistakable alert when a vehicle crosses them, prompting immediate corrective action.
How Do Rumble Strips Alert Drivers?

They trigger three simultaneous signals:
- Tactile: Vibration through steering and seat.
- Audible: A low, sustained rumbling sound.
- Visual: Painted markings or contrast patterns.
This multi-sensory approach ensures even drivers with impaired hearing or vision get the message.
Types of Rumble Strips
- Shoulder Rumble Strips: Placed along road edges to stop drift-offs.
- Centerline Rumble Strips: Separate opposing lanes to prevent head-ons.
- Transverse Rumble Strips: Positioned across lanes before hazards like toll booths or sharp curves.
- Edge Line Rumble Strips: Integrated into lane markings for dual visibility and vibration.
Crash Reduction and Safety Stats
- Shoulder rumble strips: 20–72% fewer run-off-road crashes.
- Centerline rumble strips: 44–45% fewer head-on collisions.
- Combined systems: 20–27% fewer fatal/serious injury crashes.
- Benefit-cost ratio: 5:1 to 54:1 (per FHWA and DOT studies).
Impact on Cyclists and Motorcyclists
While rumble strips improve motorist safety, poorly placed ones can inconvenience or endanger cyclists. Modern guidelines recommend minimum 4-ft clear shoulders for bike safety and smoother “mumble strip” designs to reduce vibration harshness.
Cost-Effectiveness in Developing Countries
For nations with tight infrastructure budgets, rumble devices offer exceptional returns. They require minimal installation time, no power supply, and last for years perfect for high-risk rural corridors.
Design Guidelines and Standards

International standards (FHWA, AASHTO, EU transport agencies) specify:
- Groove depth: 0.5 in (12.7 mm)
- Groove width: 7 in (178 mm)
- Spacing: 12 in (305 mm)
- Noise mitigation: Sinusoidal profiles reduce exterior noise by 2–3 dB.
Myths vs Facts
- Myth: Rumble strips damage tires.
Fact: They cause negligible wear; normal driving is unaffected. - Myth: They’re only for highways.
Fact: Increasingly used on rural and suburban roads.
International Adoption
- United States: 46 of 50 states standardize rumble strips.
- Sweden: 4,700 km of rural roads.
- Australia, Canada, Japan, EU: Widely implemented with localized designs.
Here’s how that section would look, keeping it clean, authoritative, and SEO-friendly while embedding the hyperlinks directly:
Sources
This article’s research is grounded in globally trusted, high-authority sources:
- Federal Highway Administration (FHWA): U.S. government research and crash-reduction data on rumble strips.
- National Cooperative Highway Research Program (NCHRP): Peer-reviewed studies on rumble strip effectiveness and design.
- Wikipedia – Rumble Strip: Historical background, global adoption details, and design evolution.
FAQ’s
Q1: Why are rumble devices placed before sharp bends?
To warn drivers to slow down and prepare for a change in road alignment.
Q2: Do rumble strips work in snow or rain?
Yes, vibration and sound still transmit, though noise may be dampened.
Q3: Can electric cars still feel rumble strips?
Absolutely, the tactile feedback is mechanical, not engine-related.
Q4: Are there quiet versions?
Yes, sinusoidal “mumble strips” reduce exterior noise while maintaining driver alerting.
Q5: Do they harm motorbikes?
No, but riders should cross them at a shallow angle for stability.
About the Author
Ethan K. Rowden is a Highway Safety Specialist with 12 years of experience in roadway design and crash prevention. He has advised transportation agencies in the U.S., Sweden, and Australia on implementing cost-effective rumble device systems that save lives.
GENERAL
Myloxarindor Qylendrithal: Unlocking the Meaning Behind the Mystery

Myloxarindor qylendrithal is a term that immediately sparks curiosity. It sounds rare, complex, and almost mythical. Whether you encountered it in a creative discussion, a fictional setting, or as part of a conceptual idea, this phrase carries a sense of depth and imagination. In this article, we explore what myloxarindor qylendrithal represents, its possible origins, and why it is gaining attention in creative and digital spaces.
The Concept Behind Myloxarindor Qylendrithal
At its core, myloxarindor qylendrithal appears to symbolize something abstract and imaginative. The structure of the phrase suggests fantasy-inspired language, possibly rooted in world-building or speculative fiction. Many unique terms like this are created to represent powerful forces, hidden knowledge, or advanced civilizations in storytelling. The layered sound and rhythm give it a mystical tone that feels intentional and artistic. In creative writing and branding, such distinctive phrases help build identity and intrigue. Myloxarindor qylendrithal stands out because it feels both ancient and futuristic at the same time.
Possible Origins and Linguistic Style
The linguistic style of myloxarindor qylendrithal hints at constructed language patterns often used in fantasy literature and science fiction. Writers frequently develop fictional languages to add realism and depth to imaginary worlds. The phonetic structure resembles high fantasy naming conventions, where syllables are extended and dramatic. This technique enhances immersion and emotional impact. It may also reflect elements of symbolic naming, where the sound of a word carries as much weight as its meaning. As a coined term, myloxarindor qylendrithal demonstrates how language can be shaped creatively to evoke mystery and power.
Creative and Digital Applications
In modern digital culture, unique phrases like myloxarindor qylendrithal can be used for branding, storytelling, gaming, or artistic projects. A distinctive name gives creators a competitive edge by ensuring originality and memorability. For online communities, fantasy games, or fictional universes, such a term can represent a kingdom, artifact, philosophy, or energy source. It may also serve as a symbolic concept in digital art or immersive narratives. Because it is uncommon and highly original, it holds strong SEO potential as well. Unique keywords often rank more easily when paired with meaningful content and strategic optimization.
Symbolism and Interpretative Meaning
The meaning of myloxarindor qylendrithal can be interpreted in many ways depending on context. It might symbolize transformation, hidden wisdom, or a powerful realm beyond ordinary perception. The layered sound of the phrase gives it an almost ceremonial feel, suggesting importance and depth. In speculative storytelling, names like this often represent ancient forces or lost civilizations. Symbolic language allows readers to project their own meaning onto the term, making it flexible and imaginative. This openness adds emotional resonance and creative freedom.
Why Unique Terms Like This Matter
In an era dominated by repetitive content, originality is valuable. Myloxarindor qylendrithal demonstrates the power of creative language in building strong identity and differentiation. Unique terminology strengthens brand presence, supports world-building, and enhances memorability. It encourages deeper engagement because people naturally want to understand what unfamiliar words mean. From a search engine perspective, distinctive phrases reduce competition and increase visibility. More importantly, they inspire creativity and intellectual exploration.
Conclusion
Myloxarindor qylendrithal is more than just an unusual phrase. It represents imagination, linguistic creativity, and the power of unique expression. Whether used in storytelling, branding, or conceptual design, it carries depth and intrigue. In a crowded digital world, originality stands out—and this term embodies that principle perfectly. By embracing creative language like myloxarindor qylendrithal, writers and creators open doors to new ideas and limitless possibilities.
FAQs
What is myloxarindor qylendrithal?
It is a unique, imaginative term often interpreted as a symbolic or fantasy-inspired concept.
Is myloxarindor qylendrithal a real word?
No, it appears to be a coined or constructed phrase rather than a dictionary term.
Where can myloxarindor qylendrithal be used?
It can be used in creative writing, gaming, branding, or digital storytelling projects.
Why are unique phrases like this important?
They help create originality, improve memorability, and strengthen identity.
Does myloxarindor qylendrithal have a fixed meaning?
No, its meaning depends on context and creative interpretation.
GENERAL
American Lifestyles: A Closer Look at Culture, Work, and Everyday Living

American lifestyles are often described as dynamic, diverse, and constantly evolving. From busy urban centers to quiet rural towns, life in the United States reflects a blend of tradition and modern ambition. The country’s size, cultural diversity, and economic opportunities shape how people live, work, and spend their free time. While no single definition fits everyone, certain patterns stand out in American lifestyles, including a focus on independence, career growth, innovation, and personal freedom. Understanding these elements helps explain how Americans approach daily living and long-term goals.
Cultural Diversity and Identity
One of the strongest features of American lifestyles is cultural diversity. The United States has long been shaped by immigration, bringing together people from different backgrounds, languages, and traditions. This multicultural environment influences food, music, fashion, holidays, and even communication styles. Cities like New York City and Los Angeles are prime examples of cultural blending, where communities celebrate both American traditions and their heritage.
This diversity encourages openness and creativity in everyday life. Families may celebrate Thanksgiving while also observing cultural festivals tied to their ancestry. As a result, American lifestyles often combine global influences with local customs. Identity becomes personal rather than fixed, allowing individuals to express themselves freely through lifestyle choices, careers, and social circles.
Work Culture and Career Focus
Work plays a central role in shaping American lifestyles. Many Americans prioritize career growth, entrepreneurship, and professional achievement. The idea of the “American Dream” still influences how people view success, often linking it to financial stability, homeownership, and upward mobility. Long working hours and competitive industries reflect a strong work ethic that values productivity and ambition.
At the same time, modern shifts have changed workplace culture. Remote work, digital entrepreneurship, and the gig economy now allow more flexibility. Professionals in cities like San Francisco often work in technology-driven environments, while others pursue freelance careers from home. This blend of hard work and innovation continues to shape American lifestyles, balancing ambition with new approaches to work-life balance.
Family Life and Social Values
Family structures in the United States vary widely, reflecting social change and personal choice. Nuclear families, single-parent households, blended families, and same-sex couples all contribute to the country’s social landscape. Respect for individual decisions is a core part of American lifestyles, giving people the freedom to define what family means to them.
Community involvement also plays an important role. School events, neighborhood gatherings, and volunteer work help build social connections. While independence is valued, Americans often support local causes and charities. This balance between personal freedom and community engagement defines many aspects of social life, creating both private space and shared responsibility.
Urban vs. Suburban and Rural Living
Geography significantly shapes American lifestyles. Urban living in cities like Chicago offers fast-paced environments, diverse job markets, and vibrant nightlife. Residents often rely on public transportation and live in apartments or condominiums close to work and entertainment hubs. City life emphasizes convenience and cultural access.
In contrast, suburban areas focus on family-friendly neighborhoods, larger homes, and quieter surroundings. Rural communities offer even more space, often centered around agriculture or small businesses. These differences show how lifestyle choices depend on personal priorities such as career goals, cost of living, and preferred pace of life. Each setting reflects a different version of American living.
Food, Entertainment, and Leisure
Food culture highlights the variety found in American lifestyles. From fast food chains to farm-to-table restaurants, eating habits range widely. International cuisines thrive alongside classic American dishes, showing the impact of globalization. Dining out, food delivery apps, and social gatherings centered around meals are common parts of daily life.
Entertainment also shapes leisure time. Sporting events, music festivals, streaming platforms, and outdoor recreation offer countless options. The influence of major entertainment hubs like Hollywood has made American media globally recognizable. Whether hiking in national parks or attending concerts, Americans value recreation as a way to recharge and connect socially.
Technology and Modern Living
Technology deeply influences modern American lifestyles. Smartphones, social media, and e-commerce platforms shape communication and shopping habits. Digital payments, online education, and remote healthcare services have become normal parts of daily routines. Innovation drives convenience and efficiency in both personal and professional life.
The rapid adoption of new technologies reflects a forward-thinking mindset. Many households rely on smart home devices, streaming services, and digital work tools. This tech-driven culture supports entrepreneurship and global connectivity, making American lifestyles adaptable and future-focused. While technology brings challenges such as screen time and privacy concerns, it remains central to how people live today.
Conclusion
American lifestyles cannot be defined by a single description. They are shaped by diversity, ambition, innovation, and personal freedom. From cultural traditions and career goals to family values and technological advancement, daily life in the United States reflects constant change. Urban, suburban, and rural communities all contribute to the broader picture of American living. By understanding these elements, we see that American lifestyles are less about uniformity and more about choice, opportunity, and self-expression in a fast-moving world.
FAQs
What are American lifestyles known for?
American lifestyles are known for diversity, independence, career focus, and a strong emphasis on personal freedom and innovation.
How does culture influence American lifestyles?
Cultural diversity shapes food, traditions, social values, and identity, creating a blend of global and local influences.
Is work important in American lifestyles?
Yes, work and career growth are major priorities, often connected to financial stability and personal success.
What role does technology play in daily life?
Technology supports communication, remote work, entertainment, and online services, making life more connected and efficient.
Do all Americans live the same way?
No, lifestyles vary widely depending on location, culture, income, and personal choices, reflecting the country’s diversity.
GENERAL
Balabusta Magazine: Where Culture, Creativity, and Community Meet

The Balabusta Magazine is more than just a publication; it’s a celebration of identity, heritage, and modern living. With a fresh voice and thoughtful storytelling, the magazine connects readers to culture, food, art, and strong community values. Whether you are passionate about meaningful journalism or simply love discovering inspiring stories, this lifestyle magazine offers depth without feeling heavy. It blends tradition with contemporary insight in a way that feels warm, intelligent, and refreshingly authentic.
The Meaning Behind The Balabusta Magazine
The word “balabusta” traditionally refers to a capable, strong, and resourceful woman who manages life with grace and determination. The Balabusta Magazine embraces that spirit and turns it into a powerful editorial identity. It focuses on empowered living, cultural pride, and thoughtful storytelling that resonates with modern readers. Instead of chasing trends, the magazine highlights timeless values such as family, resilience, creativity, and leadership.
Through its name and mission, the publication honors heritage while encouraging personal growth and innovation. It stands as a symbol of confidence and community strength. Readers feel represented and understood, which is why the magazine continues to build a loyal and engaged audience.
Editorial Focus and Content Style
The Balabusta Magazine covers a wide range of lifestyle topics, including food culture, family traditions, wellness, entrepreneurship, and creative expression. Its content feels carefully curated rather than mass-produced. Articles are written in a warm yet professional tone, making complex subjects easy to understand without oversimplifying them.
One of the publication’s strengths lies in its narrative journalism approach. Instead of quick summaries, it dives into personal stories, cultural insights, and meaningful conversations. Readers are not just consuming content; they are connecting with lived experiences. This storytelling style gives the magazine depth and emotional resonance.
Celebrating Food, Tradition, and Modern Living
Food plays a central role in The Balabusta Magazine, reflecting how cuisine connects generations and preserves cultural identity. Recipes are not just instructions; they are stories of heritage, memory, and family traditions. This focus on culinary storytelling adds authenticity and warmth to the publication.
At the same time, the magazine explores modern lifestyle trends, sustainable living, mindful wellness, and creative entrepreneurship. It balances nostalgia with innovation, showing readers how to honor their roots while embracing change. This unique blend makes the content relatable to both older and younger audiences.
Community, Empowerment, and Representation
A key reason why The Balabusta Magazine stands out in the crowded media landscape is its strong sense of community. It highlights voices that are often overlooked and gives space to diverse perspectives. Interviews with creators, leaders, and everyday changemakers help readers feel inspired and connected.
The magazine promotes empowerment without being overly dramatic or cliché. Its approach is subtle yet impactful, encouraging readers to take pride in their identity and pursue meaningful goals. By focusing on representation and inclusivity, it builds trust and long-term loyalty among its audience.
Why The Balabusta Magazine Stands Out Online
In today’s digital publishing world, many lifestyle platforms rely heavily on fast content and viral trends. The Balabusta Magazine takes a different path by prioritizing quality over quantity. Its long-form articles, rich storytelling, and culturally grounded themes provide real value rather than surface-level entertainment.
From an SEO perspective, the magazine integrates relevant topics such as cultural lifestyle, empowered women, food heritage, and modern community living. It maintains a natural flow of keywords without sounding forced or repetitive. This strategic yet organic approach helps it rank well while keeping the reading experience smooth and enjoyable.
Conclusion
The Balabusta Magazine is a powerful example of how modern publishing can honor tradition while embracing progress. With its focus on culture, food, empowerment, and authentic storytelling, it creates a meaningful space for readers seeking depth and connection. The publication stands out not because it shouts the loudest, but because it speaks with clarity and heart.
For anyone looking for a lifestyle magazine that feels intelligent, warm, and genuinely inspiring, The Balabusta Magazine delivers substance without sacrificing style. It proves that strong storytelling and cultural pride can thrive beautifully in the digital age.
FAQs
What is The Balabusta Magazine?
The Balabusta Magazine is a lifestyle publication that celebrates culture, food, community, and empowered living through meaningful storytelling.
What type of content does The Balabusta Magazine publish?
It covers topics such as food heritage, family traditions, wellness, entrepreneurship, and cultural identity.
Who is The Balabusta Magazine for?
The magazine is designed for readers who value culture, authenticity, strong community connections, and modern lifestyle insights.
Is The Balabusta Magazine focused on women’s empowerment?
Yes, empowerment is a core theme, inspired by the meaning of “balabusta,” which represents strength, capability, and leadership.
Why is The Balabusta Magazine unique?
Its blend of cultural storytelling, modern lifestyle content, and community-driven journalism makes it stand out from trend-focused media platforms.
-

 GENERAL7 months ago
GENERAL7 months agoRobert Hubbell Wikipedia: What’s His 2025 Biography Guide?
-

 EDUCATION9 months ago
EDUCATION9 months agoJay Kuo Substack: Unpacking the Voice of Legal Insight
-

 GENERAL9 months ago
GENERAL9 months agoDream Cake: A Decadent Delight Worth Savoring
-
 GENERAL9 months ago
GENERAL9 months agoChris Hedges Substack: A Voice of Dissent in the Digital Age
-

 ENTERTAINMENT9 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT9 months agoTyler the Creator Dad Truth
-

 TECHNOLOGY9 months ago
TECHNOLOGY9 months agoHow to Cancel Substack Subscription
-
 EDUCATION9 months ago
EDUCATION9 months agoEconomic Blackout Results: The Financial Domino Effect
-

 GENERAL9 months ago
GENERAL9 months agoMax Azzarello Substack: Inside the Mind of a Radical Truth-Seeker
